PPS Fiber Assemblies: Properties and Applications
Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS) is a high-performance polymer characterized by excellent heat resistance, corrosion resistance, and flame retardancy. PPS fibers can be continuously used at temperatures ranging from 190℃ to 220℃, and they experience almost no weight loss even in air or nitrogen environments as high as 400℃. With a stable molecular structure and sulfur (a flame-retardant element) in its composition, PPS fibers exhibit outstanding flame-retardant properties, boasting a limiting oxygen index (LOI) of up to 34. Additionally, these fibers feature low combustion rate and smoke generation, and the flame will self-extinguish once the ignition source is removed.
PPS fibers are manufactured via melt spinning. They were first commercialized by Phillips Petroleum Company of the United States in 1983 under the trade name Ryton™. As a high-performance fiber with heat resistance, corrosion resistance and flame retardancy, PPS ranks second only to polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) in chemical stability. Thus, it can meet the application requirements of harsh working conditions. In the form of fiber assemblies, PPS has demonstrated enormous application potential in fields such as industrial filtration, environmental protection, automotive industry, aerospace, and new energy.
PPS fiber assemblies were initially applied in the field of industrial filtration materials, particularly in baghouse dust collectors for high-temperature flue gas filtration. With the development of the new energy industry, PPS fiber assemblies have gradually been used in lithium battery separators and water electrolysis hydrogen production exchange membranes, which can enhance the operational safety and stability of equipment. Furthermore, PPS fiber assemblies are widely utilized in oil-water separation, chemical catalyst carriers, textile and apparel industries, among others.
Applications of PPS Fiber Assemblies
1. High-Temperature Filtration Materials
PPS fiber assemblies were first used in baghouse dust collectors of coal-fired power plants in the form of needle-punched nonwovens, and later extended to industrial sectors such as steel mills and cement plants.
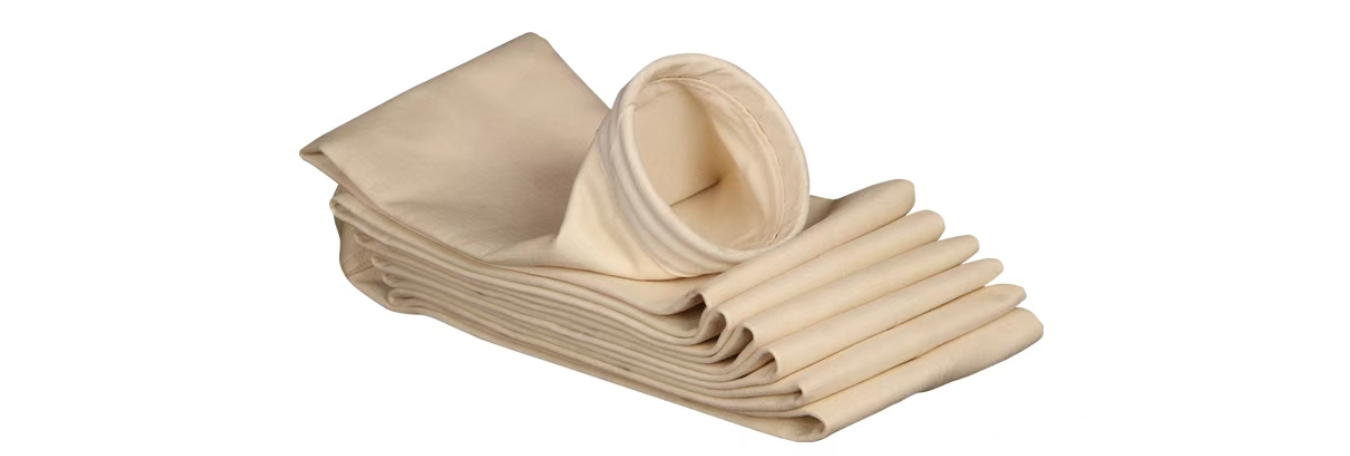

2. Battery Separators
The excellent thermal stability of PPS fibers enables them to operate at temperatures up to 200℃. This largely reduces separator shrinkage caused by thermal runaway of lithium batteries, thereby avoiding safety hazards arising from battery short circuits.
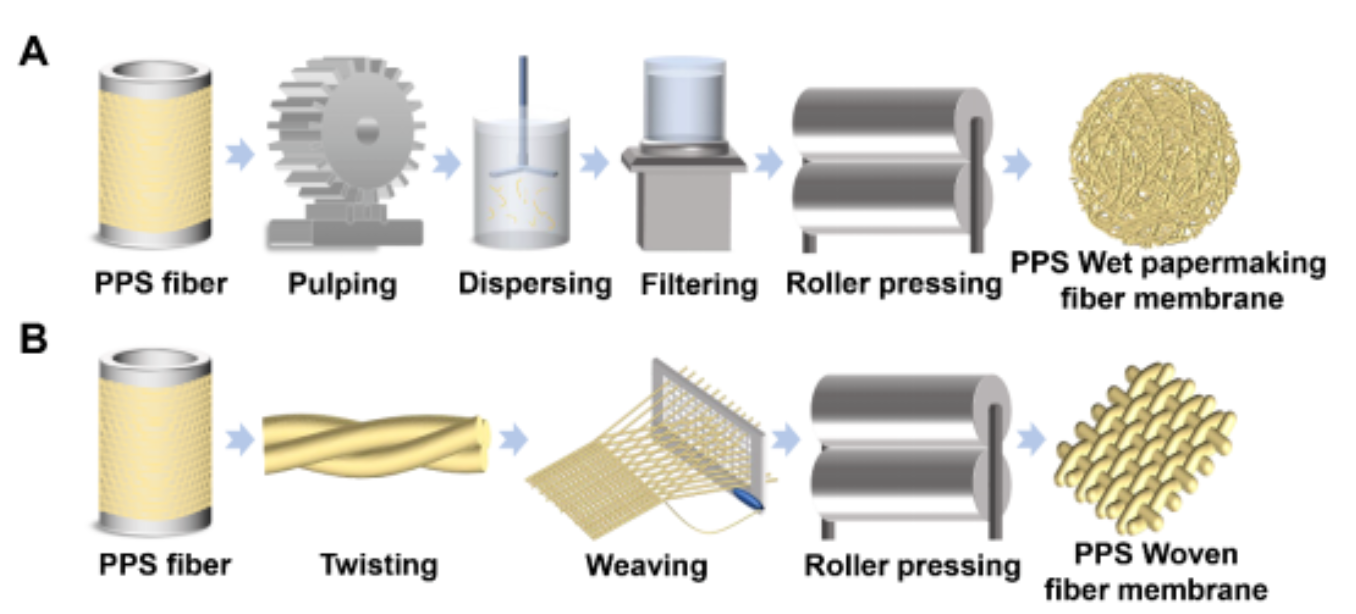
3. Hydrogen Production Membranes for Water Electrolysis
Hydrogen energy is one of the most promising clean energy sources. At present, it is mainly produced through water electrolysis technology, and the exchange membrane material between electrodes used in the water electrolysis process is PPS fiber assemblies. The high temperature resistance and chemical corrosion resistance of PPS fiber membranes perfectly meet the operational requirements of alkaline water electrolysis, which needs to work in a high-temperature and strong alkaline environment.

4. Oil-Water Separation
The treatment of polluted water, especially oil-water separation, has long been a key topic in environmental protection research. PPS fiber assemblies have shown great potential in this field. Through surface modification or differential structure treatment of PPS fiber assemblies, efficient and long-lasting oil-water separation performance can be achieved.
5. Other Applications
The superior chemical stability and heat resistance make PPS fibers an ideal material for manufacturing chemical catalyst carriers, which can effectively improve the activity and service life of catalysts. Combined with the flame-retardant property of PPS fibers, modified PPS composite fibers can be prepared by adding sodium polyacrylate (PAAS) and nano-titanium dioxide (TiO₂) to PPS. Alternatively, PPS staple fibers can be blended with other fibers (e.g., wool) to produce wearable textile materials.
